
Product requirement documents are essential assets for product teams because stakeholders often interpret product visions differently. Even when a future product seems clear to one person, each stakeholder has their perspective. Moreover, there are numerous cautionary tales of product managers who neglected effective communication on vital aspects of a new product or feature, only grasping the repercussions when it was too late.
This highlights the vital role of a Product Requirements Document (PRD). By employing a comprehensive and systematic approach, a PRD ensures alignment among all stakeholders regarding the definition of success.
In this article, we’ll delve into the essence of a PRD, explore its myriad benefits, and distinguish between a PRD and an MRD.
What Is A Product Requirements Document?
In simple terms, a Product Requirements Document (PRD) outlines the necessary features and functionalities for a specific product release. It serves as a vital guide for all teams involved in designing and developing the product, furthermore, informing the product roadmap.
Originally tailored for Waterfall methodology projects, where development progresses sequentially, however, the PRD also finds utility in agile product management.
The information within the PRD can spawn several other documents: Engineering may craft a Technical Requirements Document detailing product specifications and system requirements. Moreover, business analysts may generate a Functional Requirements Document outlining user-system interactions, often accompanied by wireframes. Furthermore, User Experience (UX) designers might develop a User Interface Requirements Document delineating the desired look and feel of the product.
When Should You Use a Product Requirements Document?
At the onset of the product development process, developing a Product Requirements Document (PRD) plays a crucial role. Once the business identifies a user need for the product, it should craft the PRD to outline the specific capabilities necessary for the release.
What are the distinctions between a Product Requirements Document and a Market Requirements Document?
The Market Requirements Document is designed to delineate the market potential or customer need for the product. It’s crucial in supporting the rationale for product development and should come before the Product Requirements Document is crafted.

A sample table of contents in a Market Requirements Document, a crucial precursor to the Product Requirements Document, is essential for establishing the business rationale behind the product. (Image Source)
The MRD typically includes a definition of the target market and presents a prioritized list of customer requirements necessary for the product’s success. This prioritized list is instrumental in shaping the core capabilities outlined in the Product Requirements Document (PRD).
Moreover, when applicable, the MRD often recommends a timeframe for the product launch to capitalize on first-to-market opportunities.
Benefits of Writing a Product Requirements Document
Investing time in crafting a comprehensive PRD offers numerous benefits. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
1. Achieving alignment among all stakeholders
A comprehensive Product Requirements Document (PRD) serves as the ultimate reference point for the diverse stakeholders engaged in product development. It meticulously outlines the deliverables, underlying assumptions, acceptance criteria, and a projected release timeline.
During the product development journey, the PRD stays dynamic, welcoming updates based on evolving customer or market demands. Its visibility to all involved parties ensures that development teams have the latest and pertinent information essential for executing the project successfully.
After the customer initially approves it, circulate the PRD among all stakeholders. Subsequently, ensure it remains easily accessible throughout the development lifecycle for necessary consultation. Utilizing a dedicated product requirements software platform streamlines consensus-building, prioritization, PRD creation, and seamless communication during product development.
2. It clarifies what falls outside the scope
Detailing significantly holds importance in what developers won’t develop, just as it does in outlining what they will develop. Product Requirement Documents (PRDs) commonly include an ‘out of scope’ section, where they enumerate features or functionalities excluded from the release.
Keeping developers aligned with time and budget constraints is the purpose of this clarification. Frequent alterations to scope often cause project failure. Choosing a more modest functionality that adequately fulfils customer requirements can often represent a prudent compromise compared to investing in an elaborate solution that requires more time and resources.
3. Encouraging collaboration among teams is one of its primary functions
Various teams collaborate and communicate to develop Effective Product Requirements Documents (PRDs); they don’t create them in isolation.
The business and marketing teams play a crucial role in assessing market dynamics and customer needs, while also garnering support and funding from leadership.
Additionally, input from business analysis and UX teams contributes to the usability and functional aspects of the product. Engineering teams bring their expertise to ensure that the technical infrastructure supports the product’s requirements.
Collaboration across these functional areas, sometimes necessitating compromise, ensures alignment and transforms the PRD into a valuable central reference point for all teams involved.
4. At the heart of the product is the customer’s perspective
Developing products with the customer in mind may appear self-evident. However, amidst various voices, it’s often easy to lose sight of our primary focus:
The Product Requirements Document (PRD) leverages insights from the Market Requirements Document (MRD) to compile a comprehensive list of essential features and functionalities anticipated to add value to users. Extensive customer research and market analysis constitute the foundation of the MRD, ensuring a robust representation of end-users’ needs.
In cases where the customer is a business stakeholder, the PRD explicitly outlines the expected product deliverables and establishes a clear timeline for its development. Elaborate acceptance criteria delineate the requisite functionality, usability, reliability, supportability, and performance benchmarks essential for a successful product release.
What are the Essential Components of a Product Requirements Document?
Let’s quickly review the essential components that a PRD (Product Requirements Document) should include.
Metadata for the Document
The Product Requirements Document (PRD) is dynamic and may change. Utilizing suitable metadata facilitates effective tracking and storage of the document.
Objectives for the Product
A concise problem statement articulates the intended outcomes of product development, aligning all stakeholders with the overarching business objectives.
Research on Customers
Incorporate any valuable insights from customer or market research into this section, which can significantly impact the product development trajectory. You may include a reference link to the Market Requirements Document (MRD) for further context.
Features
The most critical segment of your Product Requirements Document (PRD), this section serves to catalogue all agreed-upon product use cases, capabilities, features, and functionality slated for delivery in the release. In Agile development, it may encompass user stories, supplemented by UX design notes.
Negative scope
Make sure you comprehensively outline what the release will not include. This should cover elements that we may consider for future enhancements within the scope.
Environment and System Requirements
Using input from your engineering team, detail any system and environment requirements here.
Dependencies, Assumptions, and Constraints
When developing your product, it’s essential to list the assumptions guiding its development, potential obstacles that could hinder progress, and dependencies crucial for its success.
Release criteria
This section outlines the distinct acceptance criteria determining the readiness of the product for release. These criteria typically encompass five key categories:
- Functionality: Have we met the essential functional requirements?
- Usability: Is the product user-friendly and intuitive?
- Reliability: Does the product demonstrate resilience, such as recovery from system failures?
- Performance: Does the product meet specified performance benchmarks, such as loading speed?
- Supportability: Do common user systems adequately support the product?
Success Metrics
In alignment with your product objectives, this section outlines the metrics crucial for evaluating the success of your product. This involves defining parameters such as the frequency of user interactions with specific product features. Utilizing product analytics software facilitates the monitoring of user engagement and interaction patterns.
Timeline
In this section, specify the target release date for the project. While allowing for flexibility to accommodate changing requirements, it’s crucial to avoid excessive padding, as it can lead to scope creep.
What’s An Example Of A Product Requirements Document?
Here’s an example of a fully completed PRD to make understanding the document’s contents simpler with a visual aid.
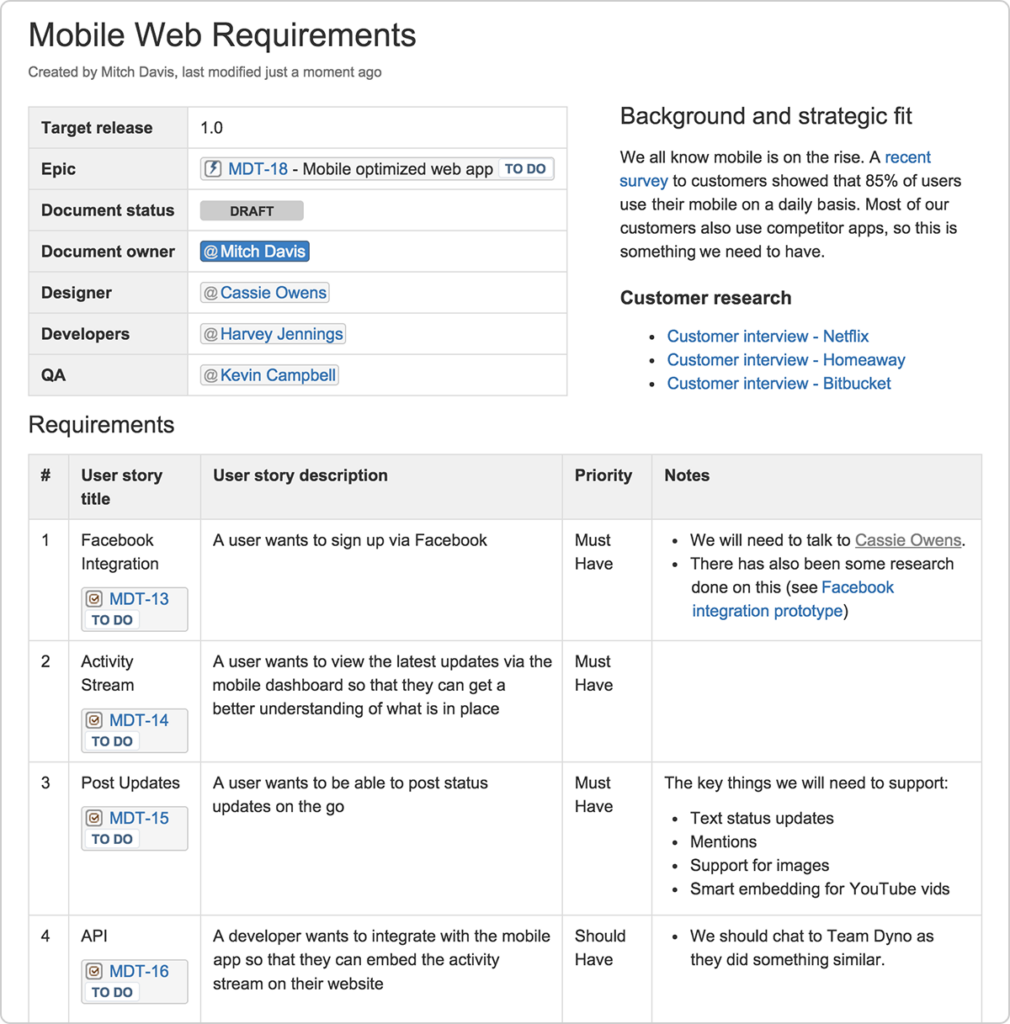

An example Product Requirements Document. (Image Source)
Best Practices for Crafting Product Requirements Documents
Now that we’ve established the essential components of a Product Requirements Document (PRD), it’s time to delve into the best strategies for assembling one effectively.
- To craft effective PRDs, it’s essential to gather input from stakeholders. The most successful product requirements documents (PRDs) emerge from collaboration with all relevant parties. Simply listing critical functionalities without consulting engineers may result in unfeasible features. Involving diverse teams from the outset fosters transparency, allowing for the identification of assumptions, constraints, and dependencies.
- As necessary, iterate. Continuous evolution drives the design of the Product Requirements Document (PRD). Evolving customer or market demands might necessitate enhancing, reorganizing, or eliminating product features. The timeline may require acceleration to secure a first-to-market advantage or extension in case of unrealized assumptions.
- Utilize version control. It’s crucial to review and update the PRD as necessary, but the product manager must have constant access to the original agreement. Employing version control and maintaining proper access levels guarantees a continuous record of the initial agreement, subsequent alterations, and the reasons behind them.
- Ensure visibility: The PRD should remain readily accessible. The document doesn’t just sit in a desk drawer after project planning; instead, it actively serves as a pivotal asset for project management. As previously emphasized, the PRD serves as a guiding reference for all team members involved in the product’s development, underscoring the importance of its continuous visibility.
- Leverage ChatGPT to handle the heavy lifting. While drafting PRDs might not be the most enjoyable task for every product manager, strategic utilization of ChatGPT can significantly streamline the process, sparing you valuable time and minimizing tedious work, provided you craft precise prompts and diligently verify its output.
Store the document centrally for easy access, enabling anyone to refer to it for clarification when necessary. Additionally, ensure that both the original document and any modified versions are available to external stakeholders.
What Are The Steps In Creating A PRD?
Creating your first PRD can seem overwhelming, despite the information we’ve provided so far. But fear not! We’re here to help. Below, you’ll find our six-step checklist to craft a robust PRD.
Get clear on the problem
Before proceeding with any other tasks, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the problem you aim to address and the specific user personas you are targeting. For the initial release, we will prioritize incorporating functionalities into the product based on this understanding.
The Business Requirements Document (BRD) should encompass a comprehensive needs statement outlining the encountered problem and the desired functionality of the product to resolve it. A thorough review of the BRD is imperative to ascertain the precise requirements of the business from the product before embarking on drafting the Product Requirements Document (PRD).

A template of a problem statement. (Image Source)
Conduct Market and User Research Review
Before crafting the Product Requirements Document (PRD), a thorough review of the Market Requirements Document (MRD) is essential. The MRD encompasses a compilation of customer requisites which will delineate the definitive capabilities of the product.
Additionally, the MRD furnishes valuable insights pertinent to UX design and business analysis teams, aiding in the determination of functional requirements.
Furthermore, the MRD plays a pivotal role in shaping the release timeline. By guiding expediting development to gain a competitive edge in the market, it influences decisions regarding feature inclusion and functionality based on timeline constraints.
Engage Functional Stakeholders
Crafting effective PRDs requires collaboration. Organize a cross-functional meeting to gather insights from various departments within the company, enriching your requirements document.
This session presents an ideal platform for stakeholders to pinpoint assumptions, voice concerns regarding risks or constraints, and highlight dependencies that might affect the product development journey.
Drafting the Product Requirements Document (PRD)
After collating information from the cross-functional meeting and integrating insights from the Business Requirements Document (BRD) and Market Requirements Document (MRD), the product manager embarks on drafting the PRD.
This involves adeptly translating customer requirements into actionable product features and functionalities, establishing release criteria and success metrics, and outlining a comprehensive timeline comprising sprints and milestones.
Afterwards, disseminate the drafted PRD among stakeholders for review. Meticulously incorporate any feedback gathered through iterative refinement of the PRD.
Obtain Approval
After completing the PRD, it’s crucial to obtain sign-off from the customer or appropriate stakeholders. This may involve the project sponsor or senior leadership team for internal projects. This step is vital for ensuring alignment with business goals and garnering support for the product development journey.
Acceptance of the release criteria is essential to clarify the product’s expected functionality, usability, and performance upon completion of the development phase. This prevents any potential misunderstandings and ensures that everyone involved understands the product’s capabilities.
Sharing and Communication
Once the PRD has received approval, it’s crucial to share its storage location and outline the process for accessing, viewing, and modifying it throughout the product development phase.
Utilize the finalized PRD as a central reference point throughout the project. It should remain dynamic, allowing real-time updates to accommodate changing requirements. However, it’s essential to maintain a clear record of the original agreement and thoroughly document any modifications, providing reasons for each change made.
Ready to unlock the potential of your product?
If you’ve diligently worked through the content provided, you’re on track to produce an outstanding Product Requirements Document.
Though it may require some initial time investment, the rewards are significant, and we are available to assist you in crafting your next exceptional product.
At Striano, we adhere to a structured process to deliver top-notch products that facilitate your company’s growth. Contact us for further information on the new software development process.